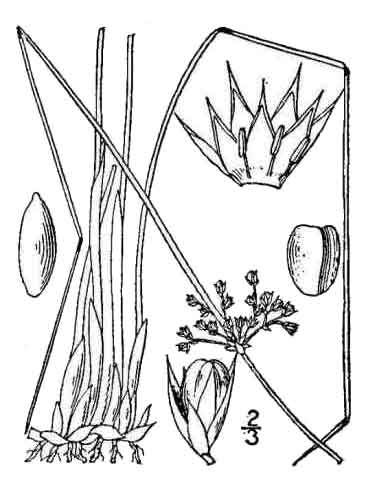
 Botany Botany
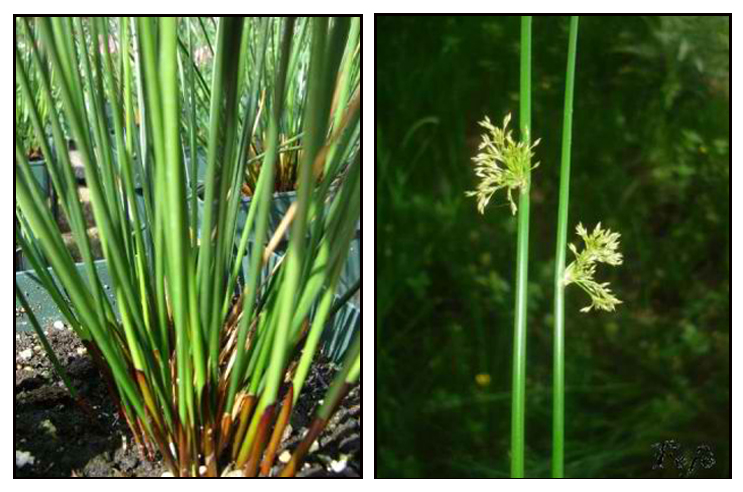
Piñgot is a plant that usually forms circular, dense, matted tufts of finely striate stems, 30 to 90 centimeters high, soft and pithy. Base of the stalk is surrounded by short, sheathing leaves. Inflorescence is very variable, lax and pendulous, with slender branches and distant flowers, or globose and sessile with densely packed flowers. Sepals are lanceolate, exceeding the length of the obovoid brownish capsules. Seeds are minute, yellow, and very obtuse at each end.
Distribution
- In open, swampy places at all altitudes from 1,400 to 2,300 meters in Luzon (Benguet, Bontoc Subprovinces).
- Also occurs in warmer parts of both hemispheres, especially common in the north temperate zone.
Constituents
 - Stems yield araban and xylan. - Stems yield araban and xylan.
-
Study isolated 13 compounds from the medullae - juncusyl ester A and B, 5-a spinasterol, B-sitosterol, effusol, p-coumaric acid, nobiletin, quercetin, rutinose, among others.
- Study isolated a new cycloartanelactone glucoside, Juncoside I.
- Dry stems yielded six phenolic constituents: 7-carboxy-2-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-vinyl-9, 10-dihydrophenanthrene, 2,3-isopylidene-1-O-ferulic acid glyceride, (2S)-2, 3-isopylidene-1-0-p-coumaroyl glycer- ide, dehydroeffusal, p-hydroxybenzaldehyde and luteolin- 5,3'-dimethyl ether.
- Study isolated 30 compounds. Six compounds were named 7-carboxy-2-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-vinyl-9, 10-dihydrophenanthrene (1), 2,7-dihydroxy-1-methyl-pyrene (2), 7-hydroxy-2-methoxy-1-methyl-pyrene (5), 2,7-dihydroxy-5-hydroxymethyl-1-methyl-phenanthrene (7), effusenone A (10), 2,3-isopropylidene-1-O-ferulic acid glyceride. The other 15 known compounds were identified as: dehydroeffusal (3), 2,7-dihydroxy-1, 6-dimethyl-pyrene (5), dehydroeffusol (6), juncusol (8),2,7-dihydroxy-1-methyl-5-vinyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene (9),β-sitosterol (11), 3β-hydroxy-5α,8α-epidiocyergosta-6E,22E-diene (12), 7-oxo-β-sitosterol (13), stigmast-4-en-6β-ol-3-one (14), (24R)-stigmast-4-ene-3-one (15), daucosterol (16), (2S)-2,3-isopropylidene-1-O-p-coumaroyl glyceride (18), p-hydroxybenzaldehyde (19), 3-hydroxy-2,5-hexadione (20), luteolin-5,3′-dimethyl ether (21). (see study below) (17)
- Study of aerial parts yielded eight phenanthrene viz. 7-carboxy-2-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-vinyl-phenanthrene (1); 2,7-dihydroxy-1-methyl-5-aldehyde-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene (2); dehydroeffusol (3); dehydrojuncusol (4); 7-carboxy-2-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-vinyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene (5); 8-carboxy-2-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-vinyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene (6); effusol (7) and juncusol (8). (see study below) (20)
- Study isolated a new sesquilignan effususin E (1) and a new long chain fatty enamide effususin F (2), along with eight known compounds from the medullae of Juncus effusus. (see study below) (21)
- Bioactivity guided phytochemical investigation yielded seven new phenanthrenoids along with nine known compounds, including eight phenanthrenoids and a benzophenone from the dichlormethane soluble fraction of ME of medullae. (see study below) (23)
Properties
- Traditionally considered antilithic, antiphlogistic, depurative, diuretic, descutient, febrifuge, pectoral and sedative.
- Seeds are cathartic.
- Studies have suggested sedative, hypnotic, cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anticancer, antioxidant properties.
Parts used
Pith, seeds.
Uses
Folkloric
- Pith is used for keeping open fistulous sores.
- Malays used the pith for urinary troubles.
- Decoction used as antilithic, pectoral and descutient.
- In traditional Chinese medicine, used for painful urination, insomnia and sleep restlessness, sore throat, and ulcerations of the mouth and tongue. Used to eliminate excessive "heart-qi" and induce urination.
- Cherokees use the herb as an herbal constituent in emetic preparations; also, used as cathartic.
- In China and Japan, folk medicine for fever, insomnia, eclampsia, and fever sores.
- Charred juncus used as sedative.
Others
• Basketry / Weaving: Stem piths used for basketry, weaving mats, and for making lamp wicks. Dried stems used for making rope.
• Paper: Fiber from stems used for making paper.
 Studies Studies
• Phenolic Contents: Ethanolic extract of the dry stem of J effusus yielded six phenolic constituents. Compounds 5 and 6, p-hydroxybenzaldehyde and luteolin-5-3'-dimethyl ester were reported for the first time. (2)
• Effusenone A / Phenolic Compounds: Study yielded a novel diterpene, effusenone A, and three novel phenolic compounds from the stem of J. effusus.
• Dihydrodibenzoxepin / Cytotoxicity: Study isolated a novel dihydrodibenzoxepin and preliminary brine shrimp lethality assay showed it to be cytotoxic. (3)
• Sedative / Hypnotic Effect: Study of extracts of JE showed influences on autonomic activity and sleeping time with pentobarbital sodium. The ethyl acetate extract showed to be the effective sedative and hypnotic fraction. (8)
• Dehydroeffusol / Anxiolytic / Sedative: Study isolated a novel phenanthrene chemical, dehydroeffusol, which showed anxiolytic and sedative properties. (9)
• Chemical Constituents / Antibacterial: Study isolated 30 compounds, six of which were new. Compound 6 (dehydroeffusol) showed antibacterial activity, with good inhibitory effect on four gram positive bacteria and Candida albicans. (12)
• Protective Effects from Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis / Root Bark: Study reports on two Chinese medical herbal extracts from roots barks of J. effusus and Paeonia suffruticosa that showed protective effect in NS-SV-Ac cells from cytotoxicity and apoptosis caused by CDDP (cis-platinum (II) diammine dichloride). Results explained the potency of the extracts as novel candidates for xerostomia in patients undergoing chemotherapy. (15)
• Anti-Inflammatory / Pith: Study evaluated the effects of ethanol extract from pith of J. effusus on anti-inflammatory activities of RAW 264.7 cells. Results showed anti-inflammatory activity by suppressing the production of inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and by attenuating edema in mice. (16)
• Antibacterial: Study isolated thirty-one compound. Compound 6, dehydroeffusol, tested against nine bacterial strains, showed good inhibitory effect on four gram + bacteria and Candida albicans. (see constituents above) (17)
• Remediation of Contaminated Mines: Water draining from abandoned mines is often highly acidic and contaminated with toxic metals. Study evaluated the remediation capacity of natural wetlands in Wales, UK. Study showed plant life might be absorbing some of the toxic elements; concentrations of iron, zinc, and copper were found reduced. The three most common plants in the wetland were soft rush (Juncus effusus), common reed (P. australis) and common cottongrass (Eriophorum angustifolium). Of these, soft rush was found to absorb the highest level of the three metals. (18)
• Phenanthrenes / Anxiolytic and Sedative: Study of aerial parts isolated 8 phenanthrenes. Compunds 7 and 8 (effusol and juncusl, respectively) showed anxiolytic and sedative activities. (see constituents above) (20)
• Cytotoxic / Anti-Inflammatory: Study isolated a new sesquilignan effususin E (1) and a new long chain fatty enamide effususin F (2), along with eight known compounds from the medullae of Juncus effusus. The new compounds, effususin E and F, were evaluated against five human cancer cell lines (SHSY-5Y, SMMC-7721, HepG-1, Hela, and MCF-7. Only compound 1 exhibited weak cytotoxic activity against SMMC-7721. Compounds 1 and 2 showed good inhibitory activity against NO production in lipopoly-saccharide-induced RAW264.7 macrophages, with IC50 of 8.59 and 13.73 µm, respectively. (21)
• Anticancer / Antioxidant / Invention: Invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition having an antioxidant and anticancer effect with an extract of Juncus effusus as an active ingredient. In the invention the ethanol extract of J. effusus was fractionated and compound 1 and 2 (dehydroeffusol and effusol, respectively) were measure for antioxidant and anticancer effect. Both compounds showed more than 90% DPPH free radical and ABTS free radical scavenging activity. Both compounds showed similar or higher inhibitory effects on cancer cell growth (human gastric cancer cell line/AGS and lung cancer cell line/A549) than anticancer drug (CPA, cyclophosphamide). (22)
• Dihydrophenanthrenes / OAT Inhibitors / Medulla: Study evaluated the interactions of J. effusus phytochemicals with human OAT1 and OAT3. Bioactivity guided phytochemical investigation yielded seven new phenanthrenoids along with nine known compounds, including eight phenanthrenoids and a benzophenone from the dichlormethane soluble fraction of ME of medullae. Compounds 10 and 16 were inhibitors of OAT1, and compounds of 1-3, 10, and 16 were inhibitors of OAT3 with IC50 values less than 5.0 µM. Dihydrophenanthrene 1 altered the pharmacokinetic parameters of the diuretic drug furosemide, a known substrate of both OAT1-and OAT-3, in vivo. (23)
• Protection of Salivary Gland Acinar Cells from Apoptotic Cell Death Induced by Cis-Platinum Diammine Dichloride / Root Bark: Study reports on the protective effect of root barks of Juncus effusus ad Paeonia suffruticosa in NS-SV-Ac cells from cytotoxicity and apoptosis caused by CDDP. Effect was dependent on p53 pathway, protein kinase B7Akt1 and mitochondrial apoptosis related protein. Results suggest potential of the extracts as novel candidates for xerostomia and to improve quality of life of patients undergoing chemotherapy. (24)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
Powders, pellets and extracts in the cybermarket.
|

![]()




 - Stems yield araban and xylan.
- Stems yield araban and xylan. Studies
Studies 