| 
Gen info
- Nephrolepis is a genus of about 30 species of ferns.
-
Etymology: The genus name Nephrolepis is Greek, meaning "kidney-shaped scales", referring to the shape of the spoor packets on the back of the fern's leaf. The species epithet cordifolia means "heart-leaf", referring to a little protrusion that looks like the bottom of a heart where the leaf (pinnule) attaches to the stem (rachis). (15)
Botany
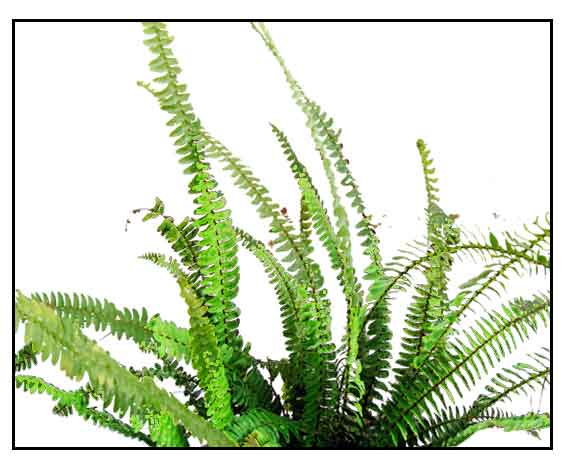
Bayabang is a terrestrial or epiphytic fern. Rhizomes are densely clothed with brownish scales, with fleshy,
egg-shaped tubers. Stipes are tufted and glossy, often clothed with slender
soft, brown paleae, 2.5 to 25 centimeters long, not jointed to rootstock. (Note:
a jointed rootstock, in contrast, breaks off very easily from its point
of attachment, leaving a more or less rounded, even-edged depression.) Fronds are simply pinnate, smooth, linear lanceolate, 20 to 60
centimeters long, 2.5 to 5 centimeters wide. Pinnae are numerous, often imbricated at the widened bases, 4 to 8
millimeters wide, the apex more or less bluntish, the base heart-shaped, jointed
to rachis, base rounded on the lower side and auricled on the upper
side, toothed to subentire. Sori are large, round, submedial, nearer the edge than the midrib. Indusium is usually reniform, broad, opening towards the apices
of the pinnae.
Nephrolepis cordifolia is an evergreen fern that grows to between 40 and 80 centimeters, in extreme cases up to 1 meter, and forming underground rhizome in the form of several small tubers. Pinnate fronds are erect and pinnate linear to lanceolate, glandular and simple. Rachis bears bicolored chaff scales. Petiole is covered with bicolored pale and dark brown scales. Leaflets are entire, sessile and elongate-lanceolate. They grow up to 4.8 centimeters long and up to 0.9 cm wide. They stand at a distance of less than 1 centimeter. Sori are rounded. Spores are warty, wrinkled. (16)
(Note: Resembles the common Boston Fern
(Nephrolepsis exaltata L.), an ornamental used extensively in flower
wreath-making, but the N. cordifolia frond is narrower.)
Distribution
- Native to the Philippines.
-
A common terrestrial fern used locally
in gardens as a hedge plant.
- Found at all altitudes in Batanes Islands in the Provinces of Bontoc, Benguet, Ifugao, Zambales, Nueva Ecija, Bataan, Pampanga, Rizal, and Laguna in Luzon; and in Cotobato, Lanao, and Zamboanga Provinces in Mindanao.
-
Also grows wild in forests and wastelands, from sea-level to above 7000 feet altitudes.
- Pantropic and tropical.
- It has become invasive in some areas. In New Zealand it is listed on the National Pest Plant Accord, which prohibits sale, cultivation, and distribution of the plant.
- Also native to Assam, Bangladesh, Borneo, Cambodia, China, Fiji, Hainan, Himalaya, India, Korea, Lesser Sunda Is., Malaya, Myanmar, Nansei-shoto, Nepal, Queensland, Sri Lanka, Sulawesi, Taiwan, Thailand, Tibet, Vietnam, etc.
(13)
 Constituents Constituents
- Tubers were found to contain high amounts of moisture, fat, carbohydrate, and calcium; protein was maximum in the rhizome part.
- Study isolated five compounds and identified as daucosteorl, palmitic monoglycerol ester, ß-sitosterol, astrafgalin and quercitrin. (10)
- Study of essential oil yielded main components of hexadecanoic acid ethyl ester,hexadecanoic acid butyl ester, n-butyl laurate, linoleic acid ethyl ester, (R) Ethyl oleate,9,12-octadecadienoic acid ethyl ester, butyl oleate,dodencanoil acid ethyl ester, cedrol,1H-3a,7-methanoazulene,2,3,4,7,8,8a-hexahyd. Â (13)
- GC-MS study of n-hexane leaf extract yielded 16 bioactive compounds
. Main compounds were n-Hexadecanoic acid (24.42%), cis-13- Octadecenoic acid (10.31%), Octadecanoic acid (11.05%), Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (8.72%), 1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis( 2-ethylhexyl) ester (18.35%) and Squalene (5.82%). (17)
- Study of hydro-distilled volatile constituents from aerial parts revealed dominant oxygenated compounds. Main constituents were ß-uibibe (8.0%), eugenol (7.2%), and anethol (4.6%).
(18)
- Phytochemical investigation of ethanolic (E), aqueous (A) and hydroalcoholic (HA) leaves extracts
yielded flavonoids, alkaloids, tannins and phenols, carbohydrates, cardiac glycosides (E and A only) and proteins.
- Proximate analysis of matured leaflets of N. cordifolia yielded moisture (86.58%), crude protein (0.78%), fat (0.34%), ash (2.50%), fiber (4.36%), and carbohydrate (7.79%).
Properties
- Faintly sweet, mildly tart.
- Cooling, stomachic, febrifuge, antitussive, tonic.
- Considered antibacterial, antitussive, styptic, antifungal.
- Studies have suggested diuretic, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, alpha-amylase inhibitory, insecticidal, anthelmintic properties.
Parts utilized
· Tubers, rhizomes, fronds.
· Collect the fleshy underground tubers, remove the epidermal
scales, wash, boil, and sun-dry.
Uses
Folkloric
- In Nepal, fresh and roasted tubers are consumed by locals. Tubers are eaten to quench thirst.
- In India, young leaves are cooked as vegetable.
Folkloric
• Decoction of fresh fronds
for fever due to cold, chronic coughing, enteritis-diarrhea, infantile
convulsions.
• In India, herb
is used for cough and skin diseases.
• In Tamil Nadu the bulb or tuber extract is taken for stomach upsets and urinary problems.
• Rhizome used as antibacterial; for coughs, rheumatism, chest congestion, anorexia.
• Pinnae used for coughs, wounds and treatment of jaundice.
• In Nepal , juice of root tubers taken for fever, indigestion, headache, cough, cold and hematuria. Whole plant used for kidney, liver and skin disorders.
• In India local tribal women use extract of rhizome once during the menstrual period to cause permanent sterility.
• In Madhya Pradesh, plants used on wounds to stop bleeding. Also used for cough and intestinal disorders, stomach ulcers and acidity. (9)
- In Nepal, tuber juice used for gastric troubles. (11)
- In Nepal, Extract of rhizome used once during menstrual period to cause permanent sterility in women. (12)
Others
- Decorative: Leaves used for decoration purposes.
- Fodder: Nutrient analysis of matured leaflets suggest source of nutrients especially for ruminants. (see study above) (24)
Studies
• Diuretic / Rhizome:
Study evaluated N. cordifolia rhizome juice for diuretic activity in Wistar rats using rhizome juice dose of 100 mg/kg. Fursosemide was used as reference drug. A single dose of rhizome juice significantly increase urine output, with increase urinary levels of Na+, K+, and Cl-. Results indicated it to be an effective hypernatremic,
hyperchloremic hyperkalemic diuretic. (1)
• Nutrient Analysis:
Study showed tubers contain high amount of moisture, fat, carbohydrate and calcium, while protein are maximum in the rhizome part of the plant. (2)
• Antibacterial Polysaccharide:
Study extract polysaccharide which was shown to have various activities against gram positive phytopathogenic microorganisms and animal pathogenic bacteria. (3)
• Antimicrobial:
In a study of pteridophytes for antibacterial and antifungal activities, the water extract of N. cordifolia showed antimicrobial properties. In another study, an ethanol extract showed marginally activity against P. mirabilis, E. aerogenes, E. coli and Klebsiella pneumonia. (5) Study of plant parts (rhizome, rachis and frond) extracts of ethnomedicinal ferns of Darjeeling viz. Nephrolepis cordifolia, Pteris vitata, and Adiantum capilus-veneris showed good antimicrobial activity. In Nephrolepis cordifolia highest activity for both gram positive and gram negative bacteria is found in the frond extract. (8)
• Hepatoprotective / Antimicrobial / Oleanolic Acid:
Study showed plant based oleanolic acid showed antimicrobial activity against vancomycin resistant enterococci with MIC of 8 µg/ml. Oleanolic acid also showed antimicrobial activity against Streptococcus pneumonia and Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Oleanolic acid also plays an important role in protection against liver injury induced by CCl4, phalloidin, acetaminophen, etc. by reducing the level of serum transaminase and preventing necrosis of liver cells. (19)
• Alpha-Amylase Inhibitory Activity / Antioxidant:
Nephrolepis cordifolia fruit showed highly potent DPPH free radical scavenging activity with IC50 value of 15.11 µg/ml. N. cordifolia fruit and leaves showed potent alpha-amylase inhibition in water extracts with IC50s of 0.49 mg/ml and 0.77 mg/ml, respectively. The fruit and leaves showed better glucose diffusion inhibition at lower concentration. (20)
• Antioxidant / Anti-Inflammatory / Leaves:
Study evaluated the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of ethanolic extracts of leaves of N. cordifolia using DPPH and HRBC (human red blood cell) methods. In the antioxidant assay, results showed 67.02% inhibition at concentration of 30 µg/ml. In HRBC, at concentrations of 250 and 500 µg/ml the leaf extract showed promising effect with 59.95 and 82.66% inhibition, respectively. Docking studies showed compound 2 was more potent than diclofenac sodium with binding energy -8.5 and -5.96 kcal/mol, respectively. (see constituents above) (21)
• Insecticidal against Whitefly A. rugioperculatus:
Study evaluated aqueous extracts of ferns for efficacy in control of whitefly, A. rugioperculatus at different concentrations under laboratory conditions. Nephrolepis cordifolia exhibited 86% mortality rate at 5% concentration after 96 hours of treatment. (22)
• Anthelmintic / Leaves:
Study evaluated the anthelmintic activity of aqueous extract of leaves against Indian earthworm Pheretima posthuma. Albendazole was used as reference drug. Results showed anthelmintic activity as evidenced by decreased paralyzing time and death time at concentration of 10 mg/ml. (23)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
Common garden hedge plant.
|


![]()

