  Gen info Gen info
- Dracaena is a genus of about 200-220 species of trees and succulent herbs. The formerly accepted genera Pleomelle and Sansevieria are now included in Dracaena.
- Dracaena species have two growth types: arborescent
(tree- or shrub-like) dracaenas i.e., Dracaena cinnabari, D. draco, D. fragrans, which have stout above-ground stems that branch from nodes after flowering or when the growth tip is severed; and rhizomatous dracaenas i.e., Dracaena angolensis, D. trifasciata, which have underground rhizomes and leaves on the surface, ranging from straplike to cylindrical. (17)
- Etymology: The genus name Dracaena derives from the Ancient Greek word drakaina, meaning "female dragon", referring to the resinous sap produced by some species in the genus, which is known as "dragon's blood". The specific epithet angolensis is Latinization of Angola, referring to the plant's origin from Angola, where it was first discovered.
Botany
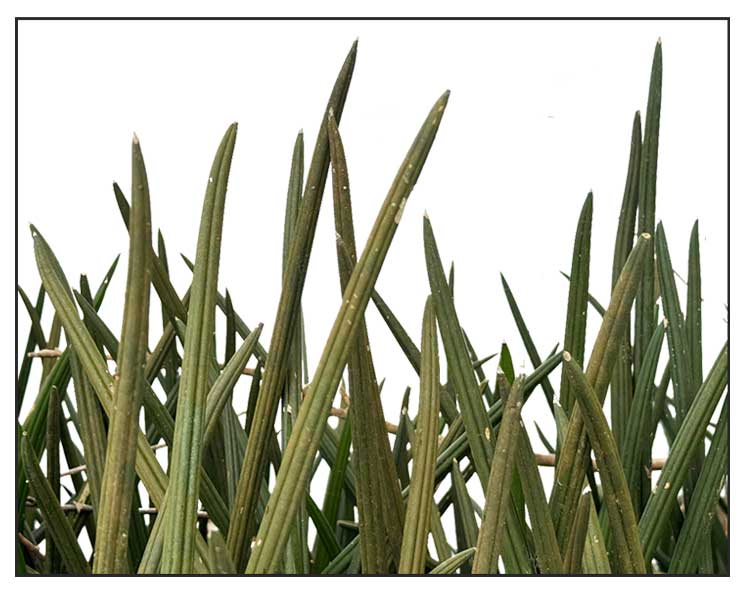
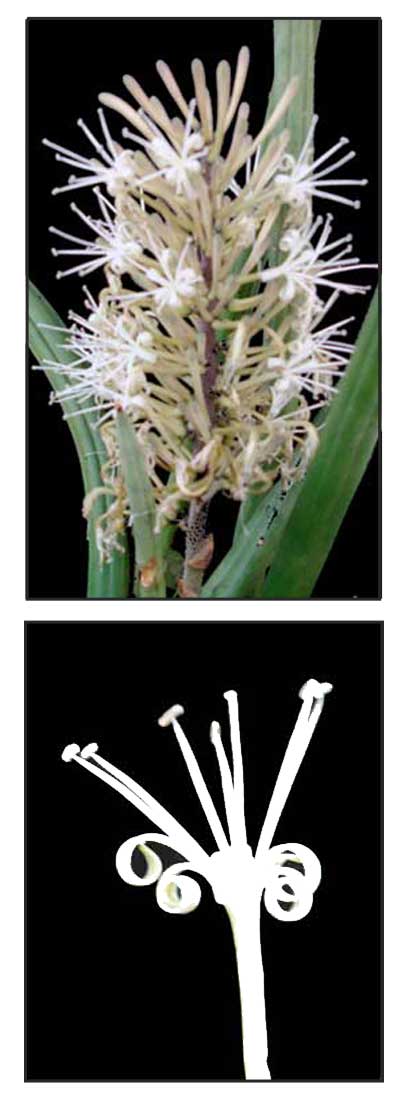
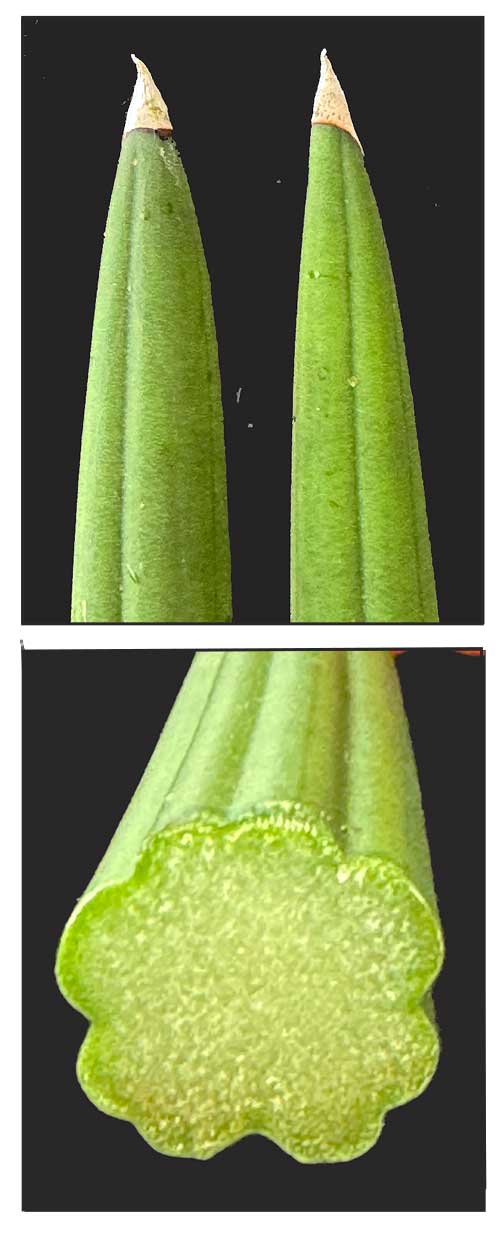
• Espada is a cylindrical, succulent perennial herb. Leaves are are green, swordlike, cylindrical and rigid, furrowed or grooved along its entire length, with pointed tips, sometimes with a dark green striped pattern, growing to a height of 2 feet or more, up to about 3 centimeters thick. Flowers are very small, white, fragrant, and crowded in
small inflorescences (cymes), greenish or tinged with red, blooming once a year.
• Growth form: Rhizomatous succulent with rod-like leaves that alternate to form a fan-like shape, growing up to 0.9 - 1.2 m tall and 0.6 - 0.9 m wide. Foliage: Stiff, cylindrical leaves taper to a sharp point and have a ribbed surface (0.6 - 1.5 m long, 2 - 3 cm wide). Leaves are greyish green with indistinct dark green bands that create a striped pattern. Flowers: White, fragrant flowers are tubular with 5 linear lobes curled backwards (2.5 cm long). The long, white stamens extend well beyond the lobes. Flowers are arranged in a whorled pattern along a spike-like inflorescence that is actually a raceme. (Flora & Fauna Web)
Distribution
- Recently introduced to
the Philippines.
- Planted as an ornamental.
- Native to Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe. (2)

Constituents
- Microstructural analysis of leaves of S. cylindrica showed the presence of structural fibers and arch fibers. (4)
- Study yielded three steroidal saponins from aerial parts.
- Study of methanol extract of aerial parts isolated a new steroidal saponin, β-hydroxy-kryptogenin-1-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 → 2)-α-l-arabinopyranoside (1), a new homoisoflavanone, (3S)-3,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxy-3-(3′,4′-methylenedioxybenzyl) chroman-4-one (2) and the known saponin alliospiroside A (3). (see study below)
(8)
- Phytochemical screening of leaves yielded steroids, flavonoids, saponins, tannins, and phenolic acids. (see study below) (9)
- Study of aerial parts isolated a new dihydrochalcone (1) and two new steroidal saponins (2 and 3), along with three known steroidal saponins (4-6). (see study below) (10)
- Proximate analysis of air-dried nonflowering aerial parts yielded a moisture content of 7.52%, total ash 9.83%, water soluble ash of 2.94$, acid-insoluble ash 3.42%, crude fiber content of 13.43%, and methanolic extractive value of 35%. Phytochemical screening of extract yielded sterols, carbohydrates and/or glycosides, flavonoids, coumarins and saponins. Total phenolic content was 4.82 mg GAE/g, and total flavonoid content was 5.13 mg QE/g d.w. (see study below) Â (11)
- Study of rhizomes isolated a new sappanin-type 3-benzyl chroman-4-one (homoisoflavanone), (3S)-3-(4'-methoxybenzyl) -3,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-6-methyl chroman-4-one (1), together with known congeners (3S)-3-(4'-methoxybenzyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxy chroman-4-one (2), (3S)-3-(4'-hydroxybenzyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-6-methyl chroman-4-one (3), (3S)-3-(4'-hydroxybenzyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxy chroman-4-one (4), 3-(3’,4'-methyledioxybenzyl)-7-hydroxy-8-methoxy chroman-4-one (5), and stigmasterol and ergosterol peroxide, along with the first isolation of (-)-enantiomer of the dihydrochalcone trifasciatine C (7) from nature.(see study below) (13)
 Properties Properties
- Study of Sansevieria cylindrica showed the flexural modulus of Sansevieria cylindrica fiber composite is much higher than those of jute or silk fiber composites. (see study below) (3)
- Considered diuretic, laxative, anthelmintic, anti-rheumatic.
- Studies have suggested
anti-trypanosomal, air-purifying, capillary permeability inhibitory, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiulcer, cytotoxic, anticancer, antidiabetic, radical scavenging, antibacterial properties.
Parts utilized
- Leaves, tubers.
Uses
Edibility
- Decoctions and infusions of leaves and roots reportedly used for making refreshing beverages in some African and Asian countries. However, it is also reported to be "mildly toxic" if eaten. Advice is to keep away from children and pet animals.
Folkloric
- In the Philippines, used for asthma, abdominal pains, colic, diarrhea, hemorrhoids. cough, rheumatism, among others. (15)
- Used as anthelmintic, laxative, and diuretic.
- In Myanmar, used for dysentery and diarrhea. (6)
- In Sri Lanka, used for snake bites, dental caries, headache.
- In various African and Asian countries, leaves used for treatment of various ailments, including coughs, diarrhea, hemorrhoids, chickenpox, rheumatism, gynecological problems, snakebites, and for wound healing. (15)
- In Lampung and Lubuk Linggau, leaves and rhizomes used for treatment of cough,, asthma, eczema, edema, malaria, anuria. In Purwakarta, used for treatment of viral hepatitis, weak sexual function, high blood pressure, hemorrhoids, colic, jaundice, palpitations, and insect and snakebites. In South Sulawesi and Buton, leaves used for coughs, flu, and diarrhea. In Central Sulawesi, roots used for snakebites. In Yogyakarta, used as air freshener, pollution absorber, and for treating wounds, bruises, and sprains. Also used as hair tonic, natural antibiotic, and pain reliever. (15)
Studies
• Steroidal Saponin / Inhibition of Capillary Permeability: Study yielded a new
steroidal saponin from the leaves of Sansevieria cylindrica. The saponin showed no haemolytic effects in the in vitro assays
and demonstrated inhibition of the capillary permeability activity. (1)
• Air Cleaning Plant: Sansevieria species are believed to have air purifying properties, removing indoor toxins like formaldehyde, trichlorethylene, benzene, xylene, toluene.
• Natural Fiber / Potential Commercial Applications: Study evaluated the tensile, flexural and dielectric properties of composites made by reinforcing Sansevieria cylindrica as a new natural fiber into a rubber based polyester matrix. Results showed Sansevieria cylindrica with a unique dielectric strength with potential for electrical insulation applications, in addition to fabrication of lightweight materials in automobile building, packaging industry, partition panes, etc. (3)
• Hybrid Fibers: Study reports on use of hybrid fibers such as Sansevieria cylindrica and tamarind fruit fibers to reinforce the epoxy matrix on mechanical and thermal properties. Epoxy filled with Tf and Sc showed remarkable improved in flexural strength and modulus. Hybrid reinforcement of filler in polymer shows significant improvement in dielectric strength of composites. (4)
• Antitrypanosmoal Activity:Study showed antitrypanosomal activity against T. evansi with IC50 (µg/ml) of 208.6±29.5. (6)
• Antibacterial / Leaves: Extracts of S. cylindrica showed good antibacterial potential against Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermis and S. pyogenes and against gram-negative bacteria viz. Salmonella spp. and Shigella dysenteriae. (7) Study assessed the invitro antibacterial activity of ethanol extract of S. cylindrica against E. coli, S. aureus, and P. aeruginosa strains by disc diffusion study. Results showed antibacterial activity against the test bacteria, (14)
• Radical Scavenging Activity: Study of aerial parts yielded a new steroidal saponin (1) , a new homoisoflavanone (2), and the known saponin alliospiroside A (3). Compound 2 exhibited radical scavenging activity comparable to ascorbic acid. (see constituents above) (8)
• Antioxidant / Antidiabetic / Leaves: An ethanol extract and its methanol fraction of S. cylindrica leaves showed significant antioxidant and antidiabetic activities. The methanol fraction showed maximum phenolic content. The ethanol extract showed 80.5% inhibition of of DPPH radicals at 100 µg/mL concentration. The methanol fraction exhibited 57.9% inhibition of glucose-6-phosphatase enzymes at 100 µM concentration. (9)
• Cytotoxic Dihydrochalcone and Steroidal Saponins / Aerial Parts: Study of aerial parts isolated a new dihydrochalcone (1) and two new steroidal saponins (2 and 3), along with three known steroidal saponins (4-6). The compounds were assayed for cytotoxicity against three human tumor cell lines HT116, MCF7, and HepG2. Compound 1 showed cytotoxicity against MCF7. Compounds 1, 3, and 6 showed moderate cytotoxicity against the three cell lines while compound 66 showed marked cytotoxicities against all tested cell lines. (10)
•
Antioxidant / Anti-Inflammatory / Antiulcer / Aerial Parts: Study of air-dried non-flowering aerial parts showed no toxicity up to 1 g/kbw. Methanolic extract showed significant central and peripheral analgesic effect. On carrageenan-induced rat paw edema assay, the extract showed inhibition but lower than reference drug indomethacin. In the ulcer model induced by indomethacin, there was significant protection against ulcer formation. In thioacetamide-induced acute hepatopathic encepalopathy model, extract treated rats showed significant improvement in plasma AST and ALT. (see constituents above) (11)
• Textile Properties of S. cylindrica: Study reports on the spinning of S. cylindrica fiber to determine the physical properties of blended S. cylindrica yarn in terms of breaking force, actual blend ratio, yarn and twist direction. Results showed the blended yarn exhibited yarn realization and possessed acceptable properties comparable to polyester/pineapple and polyester/water hyacinth which have been successfully used for clothing and apparels. Study suggests other natural fibers may be blended with S. cylindrica. (12)
• Radical Scavenging / Rhizomes: Study of rhizomes isolated a new sappanin-type 3-benzyl chroman-4-one (homoisoflavanone), (3S)-3-(4'-methoxybenzyl) -3,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-6-methyl chroman-4-one (1), together with known congeners. Compounds 4 and 7 showed no significant cytotoxicity against HeLa cells. Compounds 1–4 and 7 exhibited weak radical scavenging activity (DPPH). (13)
• Anticancer / Antioxidant / Aerial Parts:Study of aerial parts isolated hydroxymethyldihydro-chalcone (1,2-seco-homoisoflavanone) (+)-2′,4′-dihydroxy-3′-methoxy-3,4-methylenedioxy-8-hydroxymethyl-dihydrochalcone, named (+)-(8S)-trifasciatine C, which showed moderate cytotoxic effects against human breast adenocarcinoma (MCF7) cells. Also from aerial parts, 3,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxy-3-(3′,4′-methylenedioxybenzyl) chroman-4-one, named (+)-(3S)-trifasciatine B, the compounds exhibited significant DPPH radical scavenging activity (IC50 35.2 µg/mL), comparable to ascorbic acid (IC50 33.3 µg/mL. (16)
• Natural Cellulose Fibers / Potential as Non-Absorbable Suture Biomaterial:Study reports on the extraction mechanical and chemical extractions of cellulose fibers from cylindrical snake grass. Following extraction, the fibers increased in cellulose and water content, while hemicellulose and lignin decreased. The extracted fibers exhibited good mechanical properties, with weight loses of 7.4% in deionized water (DI) and 13.7% in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Commercial braided silk sutures used as control showed no weight loss. Further studies confirmed outstanding mechanical properties and showed comparable biocompatibility of snake grass fibers to commercial silk sutures. Results suggest potential of natural cellulose fibers from cylindrical snake grass as alternative source of nonabsorbable surgical suture biomaterial. (18)
Availability
- Ornamental cultivation.
- Plants in the cybermarket. |



 Gen info
Gen info
 Properties
Properties 

